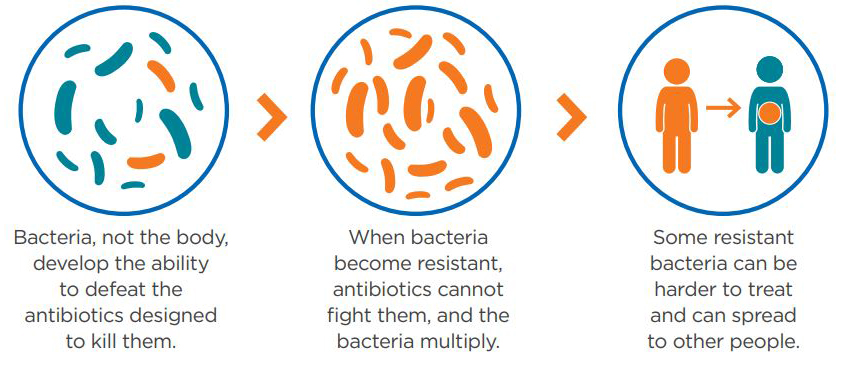
Residents/Fellows
GME General Info
Incoming Residents & Fellows
Current Residents & Fellows
GMEC
Important Links
New Innovations Policies Handbook
Programs ➔
Anesthesiology
Family & Community Health
- Addiction Medicine Fellowship
- Geriatric Medicine Fellowship
- Sports Medicine Fellowship
General Practice Residency - Dental
Internal Medicine
- Cardiology Fellowship
- Endocrinology Fellowship
- Interventional Cardiology Fellowship
- Gastroenterology Fellowship
- Hematology-Oncology Fellowship
- Nephrology Fellowship
- Nurse Practitioner Fellowship
- Pulmonary Critical Care Fellowship
Medicine / Pediatrics
Neurology
Obstetrics / Gynecology
Orthopaedic Surgery
Pediatrics
- Neonatal-Perinatal Medicine Fellowship
- Pediatric Hospital Medicine Fellowship
Psychiatry
- Child & Adolescent Psychiatry Fellowship
- Geriatric Psychiatry Fellowship
Surgery
New Innovations Policies Handbook
Departments
Administration Contacts Phone & Email Directory
Academic Departments ➔
Anesthesiology
Biomedical Sciences
Cardiovascular Services
Dentistry, Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery
Dermatology
Family & Community Health
Internal Medicine
Medical Education
Neurology
Neurosurgery
Obstetrics & Gynecology
Oncology
Ophthalmology
Orthopaedics
Pathology
Pediatrics
Psychiatry & Behavioral Medicine
Surgery
Urology
Divisions / Other Departments ➔
Animal Resources
Forensic Science
Health Science Library
Human Gift Registry / Body Donation
Information Technology
Graphic Design Services
Office of Academic Affairs
Office of Student Outreach & Engagement
Office of Faculty Advancement
Office of Student Affairs
Robert C. Byrd Center For Rural Health
Administration Contacts Phone & Email Directory