- Home |
- News |
- MUSOM News |
- Non-neuronal cells drive sex differences in early brain development
Residents/Fellows
GME General Info
Incoming Residents & Fellows
Current Residents & Fellows
GMEC
Important Links
New Innovations Policies Handbook
Programs ➔
Anesthesiology
Family & Community Health
- Addiction Medicine Fellowship
- Geriatric Medicine Fellowship
- Sports Medicine Fellowship
General Practice Residency - Dental
Internal Medicine
- Cardiology Fellowship
- Endocrinology Fellowship
- Interventional Cardiology Fellowship
- Gastroenterology Fellowship
- Hematology-Oncology Fellowship
- Nephrology Fellowship
- Nurse Practitioner Fellowship
- Pulmonary Critical Care Fellowship
Medicine / Pediatrics
Neurology
Obstetrics / Gynecology
Orthopaedic Surgery
Pediatrics
- Neonatal-Perinatal Medicine Fellowship
- Pediatric Hospital Medicine Fellowship
Psychiatry
- Child & Adolescent Psychiatry Fellowship
- Geriatric Psychiatry Fellowship
Surgery
New Innovations Policies Handbook
Departments
Administration Contacts Phone & Email Directory
Academic Departments ➔
Anesthesiology
Biomedical Sciences
Cardiovascular Services
Dentistry, Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery
Dermatology
Family & Community Health
Internal Medicine
Medical Education
Neurology
Neurosurgery
Obstetrics & Gynecology
Oncology
Ophthalmology
Orthopaedics
Pathology
Pediatrics
Psychiatry & Behavioral Medicine
Surgery
Urology
Divisions / Other Departments ➔
Animal Resources
Forensic Science
Health Science Library
Human Gift Registry / Body Donation
Information Technology
Graphic Design Services
Office of Academic Affairs
Office of Student Outreach & Engagement
Office of Faculty Advancement
Office of Student Affairs
Robert C. Byrd Center For Rural Health
Administration Contacts Phone & Email Directory

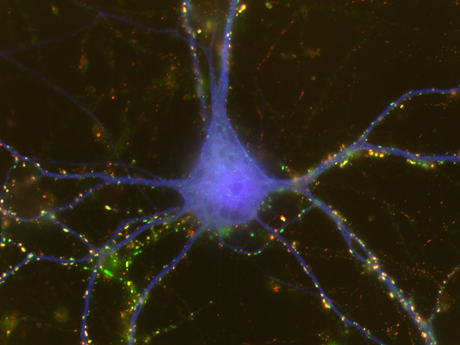 HUNTINGTON, W.Va. - During development, brain cells may find different ways to connect with each other based on sex, according to researchers at the Marshall University Joan C. Edwards School of Medicine.
HUNTINGTON, W.Va. - During development, brain cells may find different ways to connect with each other based on sex, according to researchers at the Marshall University Joan C. Edwards School of Medicine.